Hydraulic pumps are machines that can convert the energy it works with (usually mechanical or electrical) into the energy of the fluid it is trying to move. In other words, it provides the fluid with the flow rate and pressure it needs to perform a specific function.
What is a Hydraulic Pump Used For?
They have a task to providing the necessary “push” of a liquid to fulfill a specific function. Here their common uses:
- Lifting water to the top of a building (water pump)
- Extracting underground fluids (oil well or underground water pump).
- Liquid pumping through systems (as in refrigeration systems)
- Power steering in vehicles
Movement and activation of mechanical shovels (backhoe loader, Clark, dump truck, etc.).
How Do Hydraulic Pumps Work?
Hydraulic pumps are cylinders that draw liquid through rotating blades that create a suction flow. Pistons push the liquid, compress it and give it the thrust needed to reach the pressure required to perform a specific job.
Parts of a Hydraulic Pump
- Port: The cylinder into which the liquid enters the pump.
- Pistons: They are responsible for creating buoyancy and compressing the fluid.
- Crankshaft: Is responsible for generating piston movement when powered from outside.
- Starting port: The cylinder from which the liquid exits at the required pressure.
Types of Hydraulic Pumps
Hydraulic Pumps: Gear Pumps
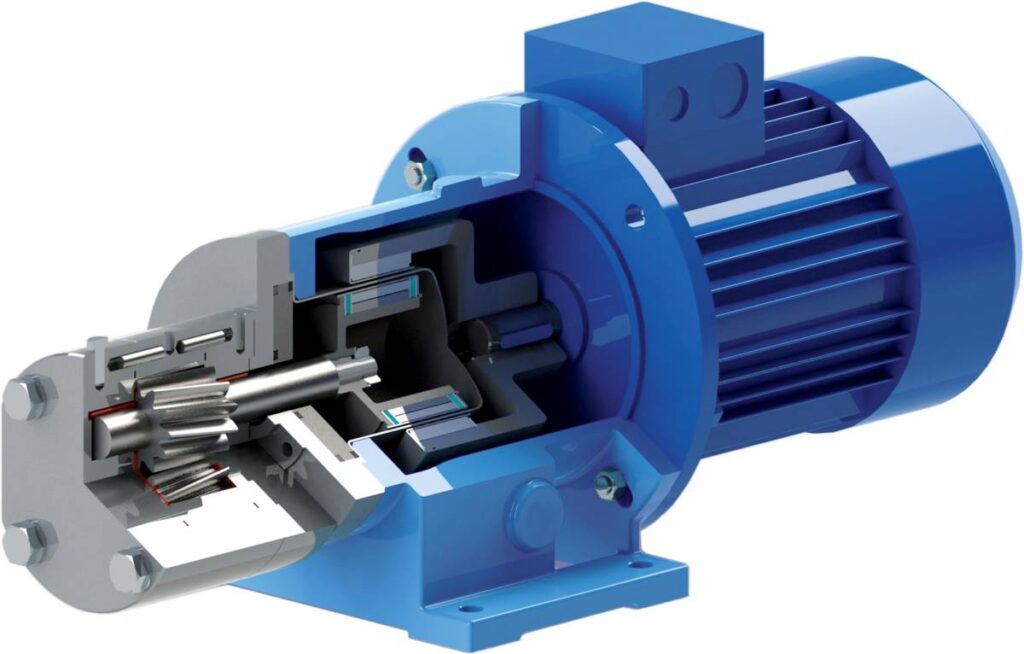
Gear pumps have very few moving parts. They consist of two interconnected gear wheels. They have a constant flow rate and generally operate at pressures between 50 and 210 bar. Gear pumps have the highest operating speeds and can reach 3000-6000 rpm.
Gear pumps are positive displacement. It’s mean that they push a constant amount of fluid per revolution. The rotating idle gear and motor assembly creates a suction at the pump inlet, and the fluid moves by pulling. The volume of fluid, directed to the discharge point between the gears, decreases with movement and increases in pressure.
Advantages:
- Reduced purchase cost
- Constant displacement
External Gear Pumps
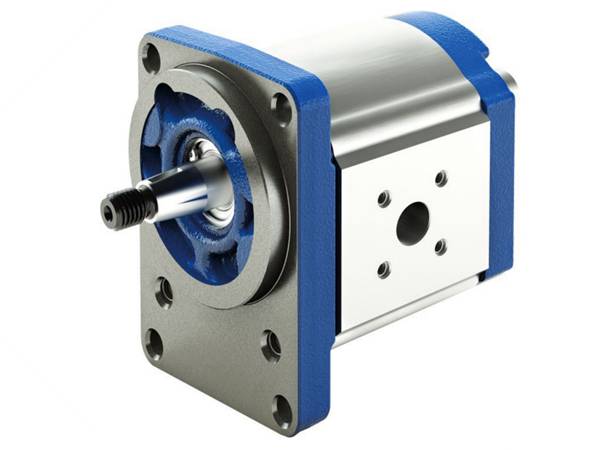

In external gear pumps, only one of the gear wheels, the driving wheel, is connected to the gearbox. The other gear wheel moves in the opposite direction by meshing with the driving wheel.
Due to the vacuum, the liquid is being absorbed in and moves to the discharge port in the tooth cavities. From the discharge port, the gears mesh with each other, creating pressure, and the liquid is discharged. The amount of liquid transported is directly proportional to the size and speed of the pump.
Internal Gear Pumps
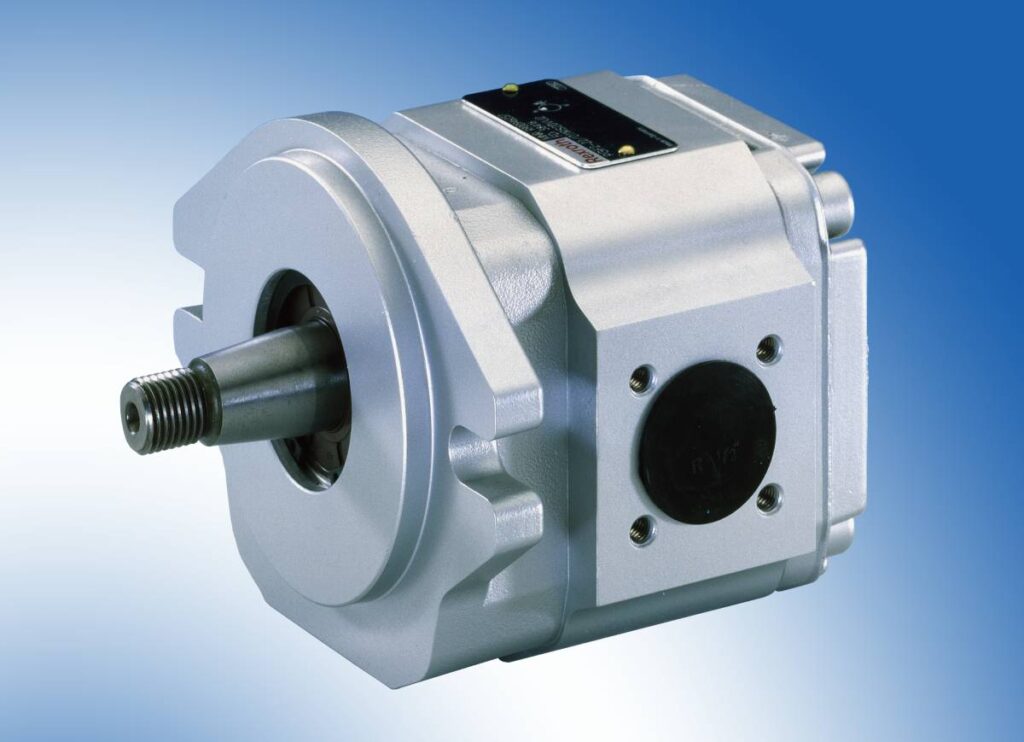

They consist of an eccentric inner gear wheel and an outer gear wheel called “crown wheel.”
As the gears rotate, when the wheels are disengaged, a certain amount of liquid is drawn in and fills the space left between the teeth of the inner wheel and the outer wheel attached to the walls of the housing.
When the teeth engage again, the liquid is ejected to the outlet-the pumping cycle is completed.
Advantages:
- Very quite
- They guarantee a constant flow rate.
What Are Gear Pumps Used For?
- Machine and engine lubrication
- Hydraulic power units
- Dosing of chemical additives
- Foam mixing in fire suppression systems
- Feeding or pressurizing diesel/naphtha
- Transfer of viscous liquids such as adhesives, paints and general grease
Hydraulic Pumps: Piston Pumps
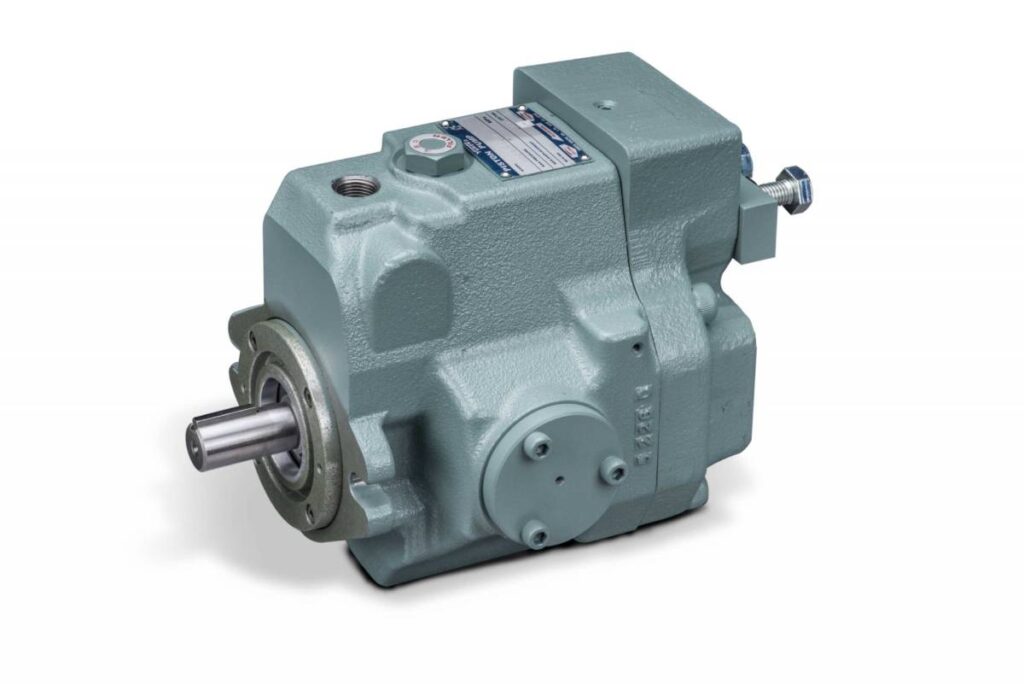

Hydraulic piston pumps can pump very high flow rates at high pressures. The principle of process is based on the alternating movement of the pistons.
Piston pumps use the alternating movement of ceramic pistons to pressurize liquids and pass them through discharge valves. The piston is usually made of ceramic, which is particularly durable and wear-resistant. In addition, they have excellent sealing properties that provide them to operate at high pressures without significant fluid loss. In piston pumps, the piston is connected to a rotor via a connecting rod so that the ceramic piston generates suction pressure when it contracts. When the rotor rotates, the piston is pushed back to push fluid through the outlet valve.
Advantages:
- Offer the best overall volumetric efficiency
- Produce higher pressures than any other type of pump.
- Reliable
- They have a high power density
- There are variable displacement models and fixed displacement models.
What Are Piston Pumps Used For?
- Pistons pumps are designed for applications requiring high pressure (400 to 700 bar), such as presses, plastics processing machines, machine tools and construction machinery.
- They are used in construction and mobile equipment, metal pressing and forming machines, machine tools and oilfield machinery.
- They are also used in water jet cutting machines. In this case, the hydraulic fluid is water, not oil.
- They are also used to pump viscous liquids such as crude oil under high pressure.
Hydraulic Pumps: Rotary Vane Pumps
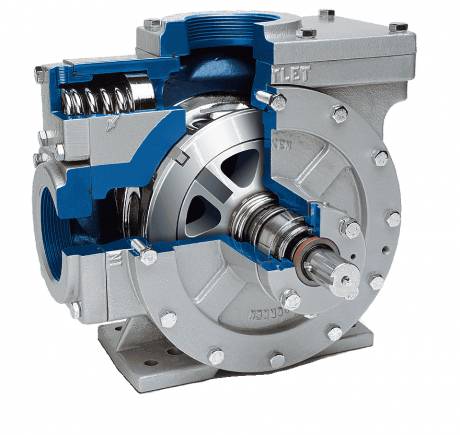

They consist of a rotor with radial grooves in which rectangular blades are placed. As a result, the blades move radially. The positive displacement vane pump is part of the positive displacement pumps. These vane pumps maintain a constant flow rate at various states of pressure. The positive displacement vane pump is also known as a self-priming pump. The liquid inside this pump is pressurized under the action of the vanes.
Advantages:
- Their volumetric efficiency is generally higher than that of gear pumps.
- They are less noisy even at high speeds (up to 3,000 rpm).
- They can have fixed or variable displacement.
- With variable displacement pumps, it is possible to reduce the flow rate if necessary and thus reduce energy consumption.
What Are Rotary Vane Pumps Used For?
Hydraulic rotary vane pumps are versatile tools that offer a wide range of uses and benefits for industrial machinery, construction sites, agricultural industries, medical environments and laboratory settings. They have ability to produce high-pressure fluid with low noise levels. So it makes them ideal for many applications, resulting in increased efficiency and productivity across all sectors.


